Prostate health is an important topic for men, particularly as they get older. However, many men feel unsure about what the prostate does, what symptoms to look out for, and when to seek medical advice. As a result, common prostate problems often go undiagnosed or untreated for longer than necessary.
The prostate is a small gland, but when it causes problems, the impact on daily life can be significant. Urinary symptoms, discomfort, sexual health concerns, and anxiety about serious conditions such as cancer are all common reasons men seek help.
In this article, we discuss the most common prostate problems, their symptoms, underlying causes, and the typical methods for investigation and management. The aim is to provide clear, reliable information in a manner that is easy to understand, while maintaining medical accuracy and professionalism.
What Is the Prostate and What Does It Do?
The prostate is a small, walnut-sized gland found only in men. It sits just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, which is the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
Its main function is to produce fluid that forms part of semen. This fluid helps protect and nourish sperm. Although the prostate plays a role in fertility, most prostate-related symptoms are linked to its position around the urethra rather than its reproductive function.
Because the prostate wraps around the urethra, any enlargement or inflammation can interfere with the normal flow of urine. This explains why common prostate problems often present with urinary symptoms.
Overview of Common Prostate Problems
Most prostate conditions fall into one of three main categories:
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) – non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate
- Prostatitis – inflammation or infection of the prostate
- Prostate Cancer – a malignant tumour of the prostate gland
Each condition has different causes, patterns, and management strategies. However, they can share overlapping symptoms, which is why proper medical assessment is essential.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
What Is BPH?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, often shortened to BPH, refers to a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. It is the most common prostate problem in men over the age of 50.
As the prostate gradually enlarges, it can press against the urethra and restrict the flow of urine. Although BPH is not cancer and does not increase the risk of prostate cancer, its symptoms can significantly affect quality of life.
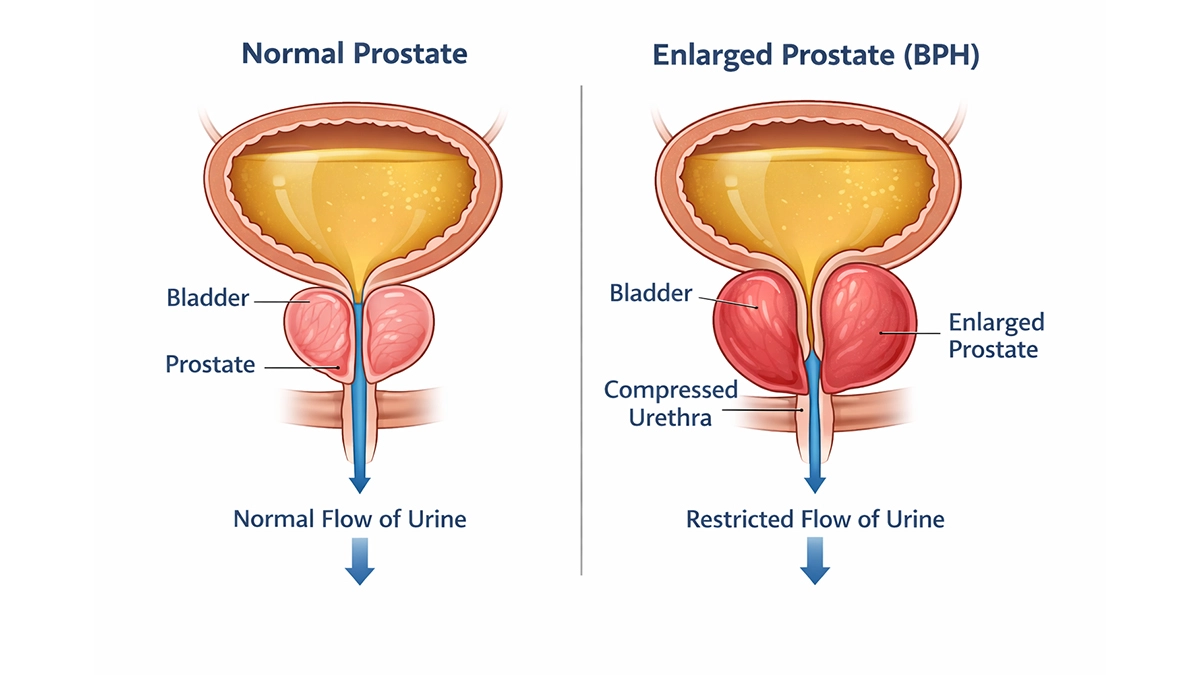
Symptoms of BPH
Men with BPH commonly experience lower urinary tract symptoms, including:
- Frequent urination, especially at night (nocturia)
- Difficulty starting and stopping urination
- A weak or slow urine stream
- A feeling that the bladder has not fully emptied
- The need to strain or push to pass urine
These symptoms tend to develop gradually and may worsen over time if left untreated.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of BPH is not fully understood. However, it is strongly linked to ageing and hormonal changes that occur as men get older.
Risk factors include:
- Increasing age
- Family history of prostate enlargement
- Hormonal changes involving testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Management of BPH
Management depends on the severity of the symptom and how much the condition affects daily life.
- Conservative management may be appropriate for mild symptoms and includes lifestyle adjustments, such as reducing evening fluid intake and limiting caffeine.
- Medical treatment often involves medications that relax the prostate or reduce its size.
- Surgical treatment may be considered if symptoms are severe, persistent, or complicated by urinary retention, infections, or bladder problems.
Further Reading: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/enlarged-prostate/
Prostatitis
What Is Prostatitis?
Prostatitis refers to inflammation of the prostate gland. It can affect men of any age, but is more commonly seen in younger and middle-aged men.
Prostatitis can be difficult to diagnose because symptoms vary widely and may overlap with other conditions. In some cases, it is caused by a bacterial infection, while in others, no clear cause is found.
Symptoms of Prostatitis
Symptoms may develop suddenly or gradually and can include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Pain in the lower back, hips, or genital area
- Frequent or urgent need to urinate
- Difficulty passing urine
- Painful ejaculation
- Blood in the semen
Because these symptoms can be distressing, early assessment is important.
Causes of Prostatitis
Prostatitis may be caused by:
- Bacterial infection
- Inflammation without infection
- Pelvic floor muscle dysfunction
In many cases, particularly with chronic prostatitis, no single cause is identified.
Management of Prostatitis
Treatment depends on the type and cause:
- Bacterial prostatitis is usually treated with antibiotics.
- Chronic prostatitis may require a combination of medication, pain management, and lifestyle measures.
Although prostatitis can be challenging to treat, many men experience improvement with appropriate care and follow-up.
Further Reading: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/prostatitis/
Prostate Cancer
What Is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is a malignant tumour of the prostate gland. It is one of the most common cancers in men, particularly in older age groups.
Importantly, early-stage prostate cancer often causes no symptoms, which is why regular monitoring and appropriate testing play a key role in detection.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
When symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Urinary symptoms similar to BPH
- Blood in the urine
- Blood in the semen
- Erectile difficulties
- Painful ejaculation
In advanced cases, prostate cancer can spread to the bones, causing persistent bone pain.
When to Seek Urgent Medical Advice
Certain symptoms require prompt medical assessment. In particular:
- Blood in the urine should always be investigated urgently.
- Persistent bone pain.
- Unexplained weight loss.
These symptoms may not always indicate cancer, but they must not be ignored.
Further Reading: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/prostate-cancer/, https://prostatecanceruk.org/
How Common Prostate Problems Are Diagnosed
Diagnosis begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Depending on symptoms, further tests may include:
- Urine tests
- Blood tests, including PSA
- Imaging scans
- Camera inspection of the bladder (cystoscopy)
- Prostate biopsy when indicated
Accurate diagnosis allows for tailored management and reassurance where appropriate.
Living With Prostate Problems
Many men live well with prostate conditions once they understand their diagnosis and treatment options. Open communication with a healthcare professional is essential.
Early diagnosis and appropriate management can significantly improve symptoms, prevent complications, and reduce anxiety associated with prostate conditions.
Prevention and Lifestyle Advice

While not all prostate conditions can be prevented, adopting a healthy lifestyle may help reduce the risk of developing prostate problems and can improve overall urinary and general health. Importantly, lifestyle measures should be seen as supportive rather than a guarantee against disease.
Diet and Prostate Health
A balanced diet plays a role in maintaining prostate health. Men are generally advised to:
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables, particularly those rich in antioxidants.
- Include foods high in fibre, such as whole grains and legumes.
- Limit processed foods, saturated fats, and excessive red meat.
- Maintain adequate hydration while avoiding excessive fluid intake late in the evening if urinary symptoms are present.
Some studies suggest that diets rich in vegetables, healthy fats, and lean proteins may support prostate health, although no single food or supplement has been proven to prevent prostate disease.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is associated with better urinary function and overall well-being. Moderate exercise can help:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Improve bladder control.
- Reduce inflammation.
- Support hormonal balance.
Men are encouraged to engage in regular aerobic activity such as walking, cycling, or swimming, alongside strength and flexibility exercises where appropriate.
Weight Management and General Health
Being overweight or obese has been linked to worsening urinary symptoms and may complicate prostate conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise can therefore be beneficial.
In addition, managing long-term health conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure supports overall urological health.
Alcohol, Caffeine, and Smoking
Lifestyle habits can influence urinary symptoms:
- Excessive caffeine and alcohol intake may irritate the bladder and worsen urinary frequency and urgency.
- Smoking is associated with poorer overall health and increased cancer risk.
Reducing alcohol and caffeine consumption and avoiding smoking can help improve urinary symptoms and general health.
Regular Check-Ups and Early Advice
Perhaps most importantly, men should not ignore urinary or prostate-related symptoms. Seeking early medical advice allows for timely diagnosis, reassurance where appropriate, and effective management before symptoms worsen.
Regular health checks and open discussions with a healthcare professional remain one of the most effective ways to protect long-term prostate health.
When Should You See a Specialist?
You should seek medical advice if you experience:
- Persistent urinary symptoms
- Pain related to urination or ejaculation
- Blood in urine or semen
- Symptoms that interfere with daily life
Early assessment allows for effective treatment and improved outcomes.
Final Thoughts
Common prostate problems are exactly that – common. While they can be worrying, many prostate conditions are manageable with the right medical care.
Understanding symptoms, recognising when to seek help, and attending regular follow-ups all play a crucial role in maintaining prostate health. If you have concerns, do not delay speaking to a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a meaningful difference to both short- and long-term outcomes.
This content is for general information only and should not be used as a substitute for personalised medical advice. Please speak to a qualified healthcare professional.
Experiencing Any of These Symptoms?
Persistent prostate or urinary symptoms should not be ignored. Early assessment by a urology specialist can provide reassurance and ensure timely treatment where needed.